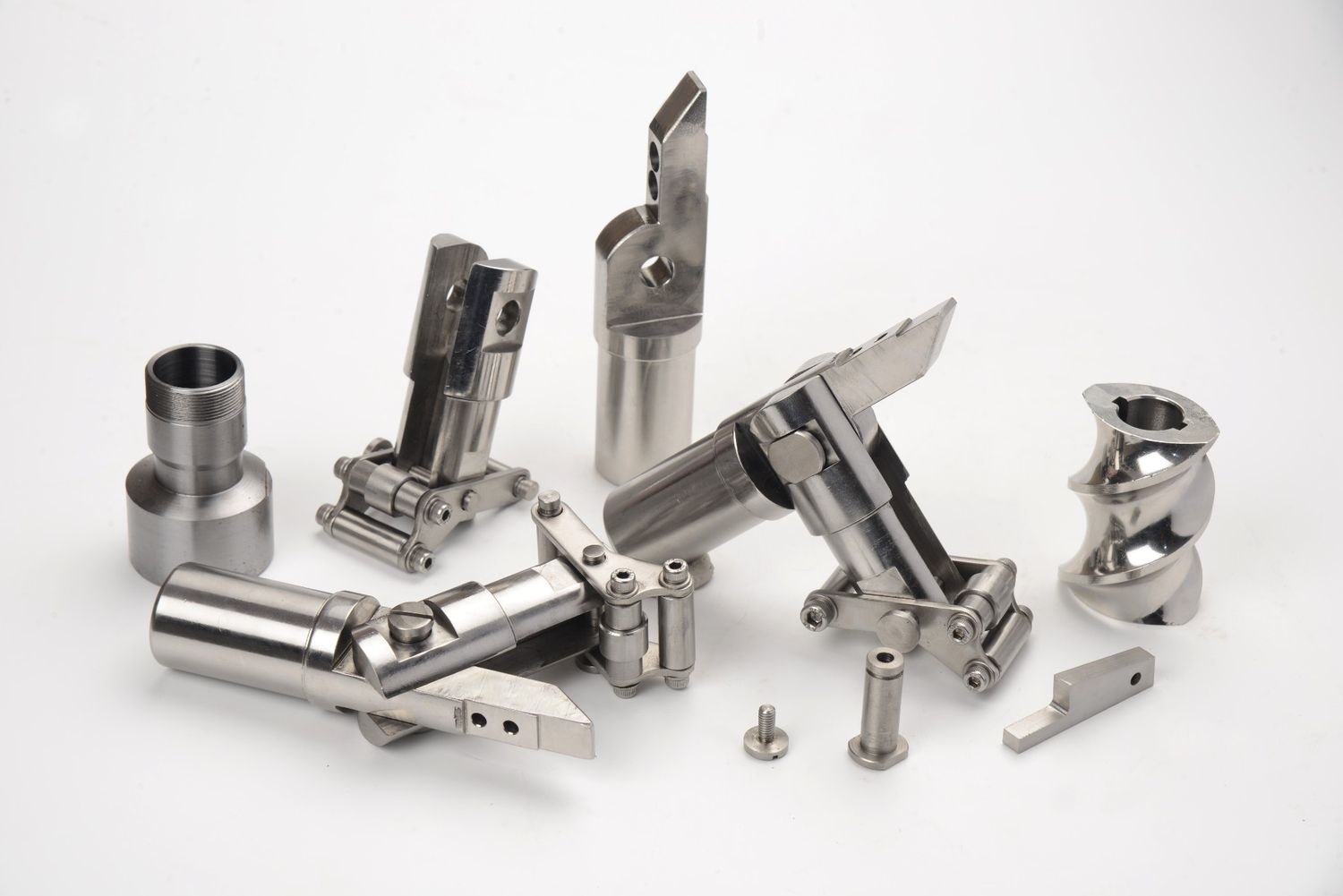
Description
Here are key aspects related to machining parts for assembly and machinery:
- Materials:
Machinery parts are made from a wide range of materials, including metals (such as steel, aluminum, brass, and alloys) and plastics. The material selection is based on factors like strength, durability, and the specific requirements of the machinery. - Precision Machining:
Precision is crucial in the production of machinery parts to ensure proper fit, alignment, and functionality. CNC machining is commonly used for precision machining, allowing for tight tolerances and high accuracy. This is important for components like gears, shafts, and bearings. - Mass Production:
Depending on the machinery and its application, parts may be produced in large quantities. Machining processes must be optimized for efficiency and repeatability to meet the demands of mass production. - Durability and Wear Resistance:
Machinery components are often subjected to wear and stress. Machining processes may include the use of special materials, heat treatments, and surface coatings to enhance durability and resist wear, especially for components like gears and moving parts. - Complex Geometries:
Machinery parts can have complex shapes and intricate geometries. Machining techniques, including multi-axis machining and precision milling, are employed to produce components with complex features, such as turbine blades, complex housings, and intricate structural elements. - Surface Finish:
The surface finish of machinery parts is important for reducing friction, preventing corrosion, and ensuring proper operation. Machining processes are controlled to achieve the required surface finish, and additional finishing techniques may be applied. - Quality Control:
Rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the machining process to ensure that machinery components meet strict industry standards. Inspection processes may include dimensional checks, material testing, and functional testing. - Customization:
Different types of machinery require different components. Machining allows for the customization of parts to fit different machinery models and meet specific design specifications. - Regulatory Compliance:
Machinery manufacturers must comply with industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards ensures the safety, reliability, and quality of machinery components.
Examples of machinery parts that may undergo machining include gears, shafts, bearings, housings, structural elements, and various internal components used in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, construction, and automotive.
In summary, machining plays a crucial role in the production of assembly and machinery parts, where precision, durability, and compliance with industry standards are essential. Advanced machining technologies and stringent quality control measures are employed to meet the specific requirements of machinery in various sectors.