Description
Here are key aspects related to machining jigs and fixtures:
- Materials:
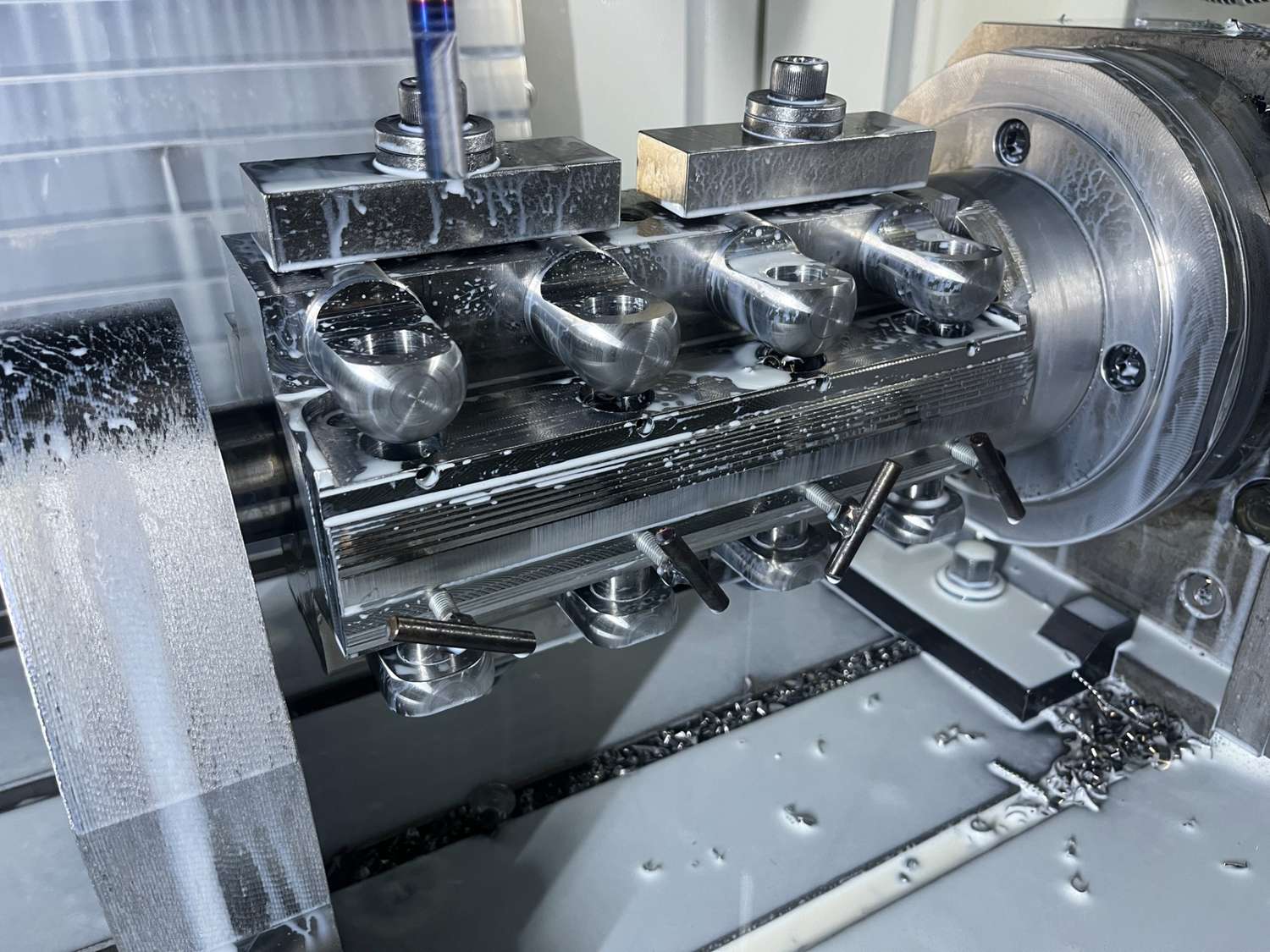
Jigs and fixtures are typically made from durable materials that can withstand repeated use and provide stability during machining. Common materials include tool steel, aluminum, and various alloys, depending on the specific requirements of the application. - Precision Machining:
Precision is critical in the production of jigs and fixtures to ensure that they hold workpieces securely and accurately during machining. CNC machining is commonly used for precision machining, allowing for tight tolerances and high accuracy. - Repeatability:
Jigs and fixtures are designed for repeatability, allowing the same machining operation to be performed consistently on multiple workpieces. Machining processes must be highly controlled to achieve the desired repeatability. - Complex Geometries:
Jigs and fixtures can have complex shapes and intricate features to accommodate the specific needs of a machining process. Machining techniques, including multi-axis machining, are employed to produce components with complex geometries. - Interchangeability:
Some jigs and fixtures are designed to be interchangeable to accommodate different parts or configurations. Machining processes must ensure the interchangeability of components for flexibility in manufacturing. - Surface Finish:
The surface finish of jigs and fixtures is important to prevent wear, reduce friction, and ensure the accurate positioning of workpieces. Machining processes are controlled to achieve the required surface finish. - Stability and Rigidity:
Jigs and fixtures need to provide stability and rigidity to securely hold workpieces during machining. Machining processes may include strategies to enhance the structural integrity of components and ensure their stability during use. - Customization:
Jigs and fixtures are often customized for specific manufacturing processes and part geometries. Machining allows for the production of tailored solutions to meet the unique requirements of different machining applications. - Quality Control:
Rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the machining process to ensure that jigs and fixtures meet the required specifications. Inspection processes may include dimensional checks and functional testing.
Examples of jigs and fixtures that may undergo machining include drill jigs, milling fixtures, welding fixtures, and assembly fixtures used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and general manufacturing.
In summary, machining plays a crucial role in the production of jigs and fixtures, where precision, repeatability, and customization are essential. Advanced machining technologies and strict quality control measures are employed to meet the specific requirements of jigs and fixtures used in various manufacturing processes.