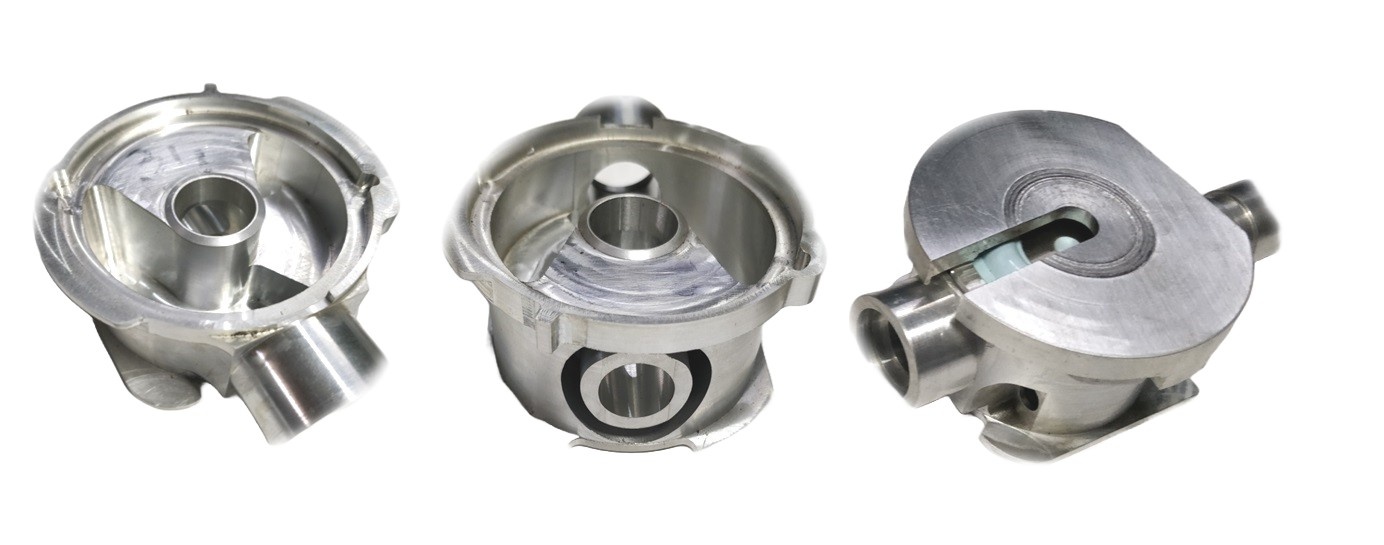
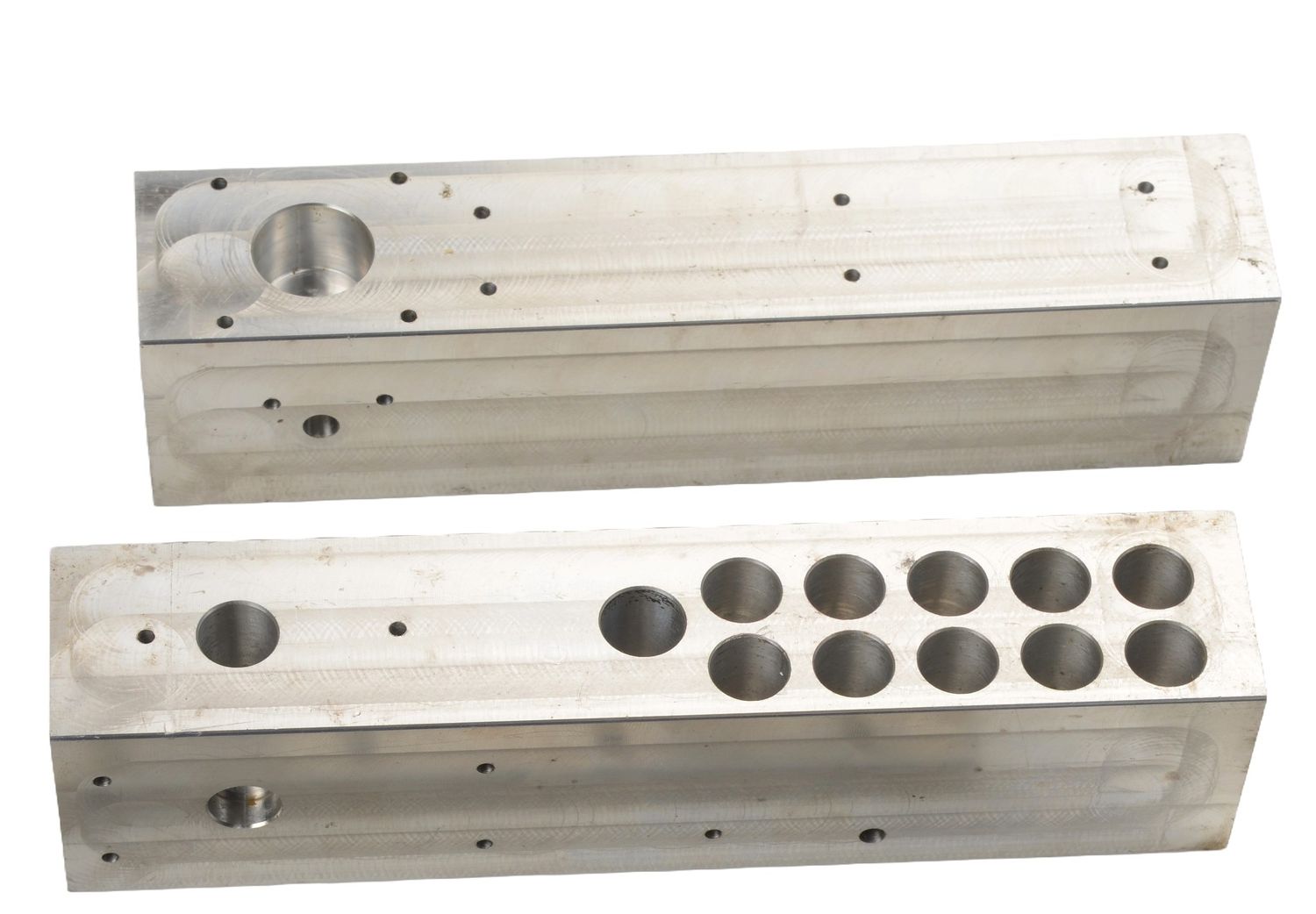
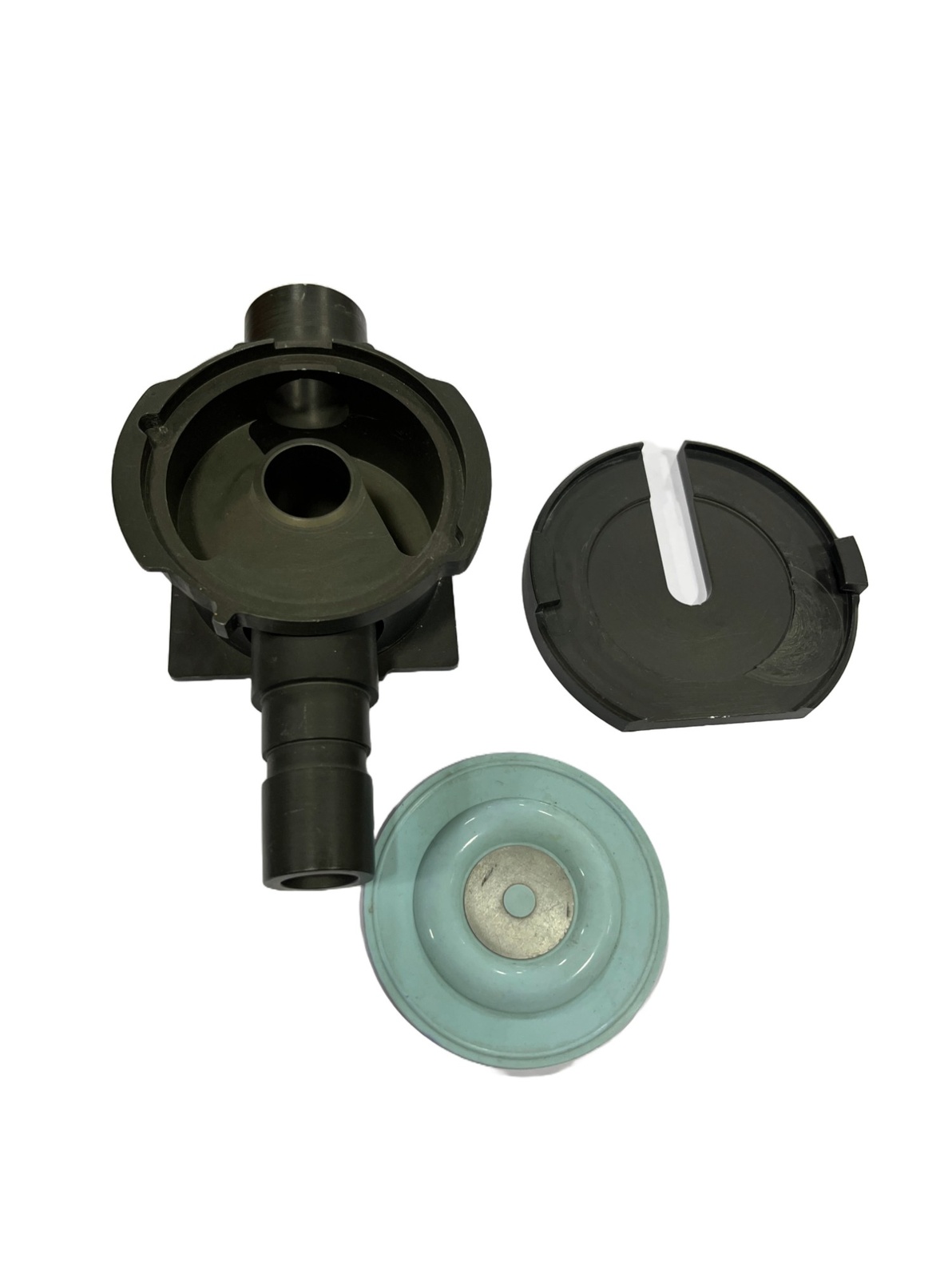
Description
Here are some key aspects related to machining biomedical equipment parts:
- Materials:
Biomedical equipment parts are often made from materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and medical-grade plastics. The selection of materials depends on factors like biocompatibility, strength, and the specific requirements of the medical application. - Precision Machining:
Precision is crucial in the production of biomedical equipment parts. CNC machining is commonly used to achieve tight tolerances and ensure accurate and repeatable manufacturing. Multi-axis machining may be employed for complex geometries. - Cleanliness and Sterilization:
Biomedical equipment parts must adhere to strict cleanliness and sterilization standards to ensure patient safety and prevent infections. Cleanroom environments and specialized cleaning and sterilization processes are often employed during and after the machining process. - Quality Control:
Rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the machining process. Dimensional checks, material testing, and surface finish inspections are conducted to meet the required specifications and comply with regulatory standards. - Customization and Prototyping:
Biomedical equipment often requires customized components to fit specific medical device designs and applications. Machining allows for efficient customization and the production of prototypes for testing and validation. - Regulatory Compliance:
Biomedical equipment manufacturers must adhere to strict regulatory standards set by health authorities, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA). Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and ISO standards is essential to ensure product safety and efficacy. - Surface Finish:
Surface finish is crucial in biomedical equipment to facilitate easy cleaning, sterilization, and to minimize the risk of infections. Machining processes are carefully controlled to achieve the required surface finish, and additional finishing techniques may be applied. - Small to Medium Batch Production:
Biomedical equipment parts may be produced in relatively small to medium-sized batches. Machining allows for efficient production while maintaining high precision and quality standards.
Examples of biomedical equipment parts that may undergo machining include components for X-ray machines, MRI systems, surgical instruments, patient monitors, and laboratory equipment.
In summary, machining plays a vital role in the production of biomedical equipment parts, where precision, cleanliness, and regulatory compliance are paramount. Advanced machining technologies and strict quality control measures are essential to meet the rigorous requirements of the medical and healthcare industries.